
Smoking is positively associated with oral thrush – in fact, it’s one of the main oral thrush causes in healthy adults. Tobacco smoke will dry your mouth, cause lesions to appear, and destroy the bacterial balance, thereby favoring nasty organisms such as candida albicans.
To better understand how smoking causes thrush, you first need to know how oral thrush appears.
How does thrush appear?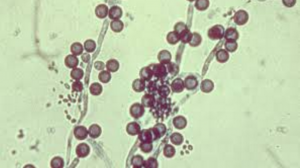
The reason why smoking causes oral thrush are easy to understand, once you know how candida albicans grows and develops.
Candida Albicans accounts for more than 50% of the oral candidiasis, and it’s the main pathogen – the infecting organism – involved in oral thrush.
The fungi is often part of the intestinal gut. So often, in fact, that about 70% of the population carries it in their intestinal flora. Though this figure may seem high, most of the time this type of candida is harmless, since it’s kept in check by the rest of the bacterial flora.
Aside from the gut, candida albicans is also present in the mouth. About 50% of the world’s population carries it and, again, it’s not usually dangerous.
The real problem comes when this organism grows to disproportionate numbers – a process known as candida overgrowth. This may be caused by a variety of factors, from a course of antibiotics to an imbalanced diet to bad oral hygiene. Several diseases also cause an increase in the population of candida albicans, such as AIDS, cancer, vaginal yeast infections and diabetes mellitus.
How does smoking cause thrush?
Tobacco smoke kills the beneficial bacteria in your mouth, thereby allowing the candida colonies to grow freely.
In fact, studies have shown that smoking causes a considerable amount of damage to the mouth tissue, while encouraging the candida colonies to grow, as a result of destroying much of the rest of the mouth flora.
Smoking is so closely associated with smoking, that it’s actually a stand-alone risk factor in patients suffering from HIV.
What can I do?
Stop smoking. If you’ve got oral thrush, smoking is the worst thing you could do.
As soon as you experience the first symptoms, consult your doctor and start treating your infection. Drugs such as Diflucan or Nystatin are pretty successful when it comes to treating thrush, and home remedies are also quite efficient.
Whatever you do, pay attention to your diet – you want to avoid sugar and yeast-rich foods, and eat plenty of probiotics, such as unsweetened yogurt.
Conclusion
Smoking is a serious risk factor for oral thrush: it damages the oral tissue, kills the beneficial organisms in your mouth, and helps spread the candida infection.
If possible, avoid smoking at all costs, especially if you’re experiencing thrush symptoms. Consult your doctor and start the treatment as soon as possible.
Resources
http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/oral-thrush/basics/definition/con-20022381
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oral_candidiasis
http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/Oral-thrush—adults/Pages/Introduction.aspx
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/969147-clinical
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16120112
http://www.nynjaetc.org/documents/ChattopadhyayandPattonOralPathology.pdf

