
Since oral thrush is cause by a fungus present in most people (candida albicans), it’s usually not contagious. However, it can be transmitted back and forth between breastfeeding mother and child, in which case both will have to be treated.
Though not contagious, oral thrush may spread to different parts of the body, leading to unpleasant infections. Read on to find out more about oral thrush and where it’s likely to spread.
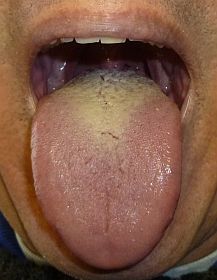
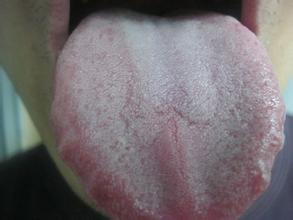
Thrush Dehydration
vs
Before taking an oral thrush treatment, you should first know if you have it or not.
Though white, creamy patches that can be scraped away are a common symptom of oral thrush, there are more causes of white tongue, and you need to consult your doctor as soon as the normal white coating of the tongue becomes too thick or uncomfortable.
In some cases, a white tongue may just be a symptom of dehydration.
Oral Thrush on the Roof of the Mouth
White patches on the roof of your mouth are a common symptom of oral thrush, and you can treat them the say way you’d treat the infection in its early stages. Remember to consult your doctor and take the treatment exactly as prescribed, to avoid any complications.
Don’t neglect thrush on your throat – chances are you won’t anyways, since it’s likely you won’t be able to eat properly – as it may be the sign of a more serious condition. Consult your doctor as soon as possible and take the treatment exactly as prescribe. Also, remember to eat properly, since candida thrives on sugars and yeast.
Oral thrush is not normally painful, but you might experience pain once the infection becomes more severe. The best way to avoid such unpleasant symptoms is to treat it as soon as you notice the first white patches – this will ensure a fast cure, and will lower the chances of the infection becoming systemic.
Conclusion
Oral thrush is not a contagious condition, but it may spread throughout your body, and it may lead to further complications. It’s best to identify it correctly and treat it as soon as you notice the first symptoms.

