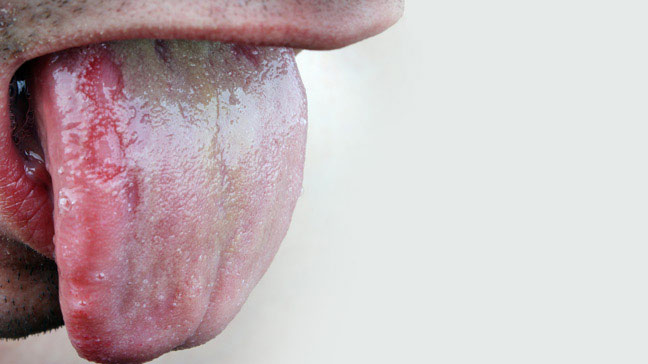
Oral thrush is a type of candida infection that’s particularly ugly looking; that’s got to have something to do with it being located in the mouth, and with all those creamy white patches that you’d much rather not see, let alone touch.
However, it doesn’t have to be as bad as you’d imagine, and it’s pretty easy to treat if you’ve got the right anti-fungal medication. In this article, we’ll show you how different stages of thrush look like, and we’ll also examine different regions where the infection might spread.
But first, let’s take a look at the main culprit: candida albicans.
Candida albicans
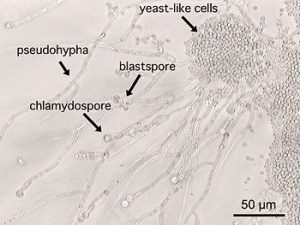 This yeast is the main cause of oral thrush. Though it’s normally present in the mouths of the majority of the population, it’s usually not dangerous until it grows to unusually high numbers. This abnormal growth can be caused by a lot of things, from a weak immune system, incapable of staving it off, to an imbalanced diet, rich in sugars and poor in probiotics such as yogurt or milk, to certain diseases such as AIDS or diabetes.
This yeast is the main cause of oral thrush. Though it’s normally present in the mouths of the majority of the population, it’s usually not dangerous until it grows to unusually high numbers. This abnormal growth can be caused by a lot of things, from a weak immune system, incapable of staving it off, to an imbalanced diet, rich in sugars and poor in probiotics such as yogurt or milk, to certain diseases such as AIDS or diabetes.
Notice how the yeast-like cells are grouped together in dense colonies. Once the overgrowth process begins, these colonies will form the creamy white patches commonly associated with oral thrush.
Early stages: inflammation and small whitish patches
In the early stages, your tongue will begin to swell slightly and some whitish patches will 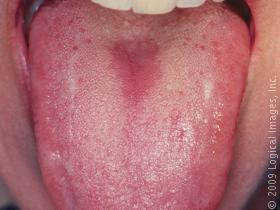 appear. They won’t be too unsightly and you may even mistake them for saliva. They’ll soon begin to spread around the tongue, though, in which case you’ll know you’re dealing with thrush.
appear. They won’t be too unsightly and you may even mistake them for saliva. They’ll soon begin to spread around the tongue, though, in which case you’ll know you’re dealing with thrush.
White lesions: the main symptom of oral thrush
As the infection develops, you’ll notice white lesions that look like milk residue, but are in 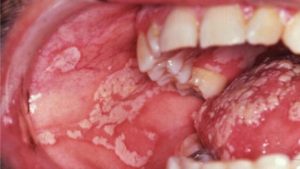 fact candida albicans colonies growing out of control. They’ll be located on the tongue, cheeks, inner lips and palate, and you should be able to scrape them off. However, doing so would probably result in slight bleeding and pain, so it’s better to deal with your infection by using anti-fungal medicines.
fact candida albicans colonies growing out of control. They’ll be located on the tongue, cheeks, inner lips and palate, and you should be able to scrape them off. However, doing so would probably result in slight bleeding and pain, so it’s better to deal with your infection by using anti-fungal medicines.
Oral thrush affecting the throat
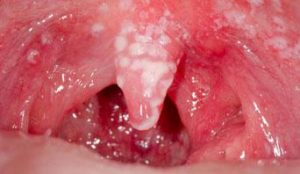 If left untreated, the infection will progress towards the throat. As it does so, these white patches will be visible deep down your throat and you’ll experience symptoms such as difficulty swallowing and a sensation of burning. You’ll probably want to avoid hot and hard foods at this points, as they’ll irritate your throat and they’ll make swallowing even more difficult.
If left untreated, the infection will progress towards the throat. As it does so, these white patches will be visible deep down your throat and you’ll experience symptoms such as difficulty swallowing and a sensation of burning. You’ll probably want to avoid hot and hard foods at this points, as they’ll irritate your throat and they’ll make swallowing even more difficult.
Laryngeal thrush
As the candida moves down, it may reach your larynx. As it does so, you’ll experience 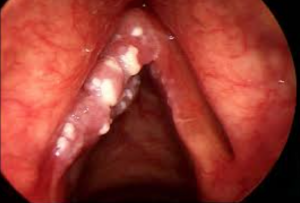 hoarseness and pain. Since the larynx is not within easy reach, you won’t be able to apply anti-fungal medication directly on it, so you’ll need to use some form of prescribed pills such as fluconazole. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
hoarseness and pain. Since the larynx is not within easy reach, you won’t be able to apply anti-fungal medication directly on it, so you’ll need to use some form of prescribed pills such as fluconazole. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Oral thrush is not a severe condition in its early stages, but it can become more unpleasant the longer it’s left untreated. We’ve shown you a few pictures of oral thrush at different stages of development and in different regions of the mouth and throat, so now you can recognize it easily – and, hopefully, before it gets too serious. Be sure to check this list of oral thrush treatment options, as there are a few ways to rid yourself of this condition.
Resources
http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/dental-health-thrush
http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/Oral-thrush—adults/Pages/Introduction.aspx
http://aor.sagepub.com/content/114/5/369.abstract
https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a690002.html

